Magsorption Water Purification: The Future of Clean and Sustainable Water Treatment
Around the world, the demand for clean, safe, and accessible water is rapidly increasing. From urban households to large-scale industries, water purification systems must evolve to meet rising environmental and health standards. One of the most promising scientific breakthroughs in recent years is magsorption water purification—a technique that combines the power of magnetic separation with advanced adsorption technology. This fusion not only enhances efficiency but also reduces waste, making it an eco-friendly and cost-effective solution for modern water treatment challenges.
In this comprehensive article, we explore what magsorption water purification is, why it is gaining global attention, how it works, and what makes it a cutting-edge innovation for both present and future applications. With over 1000 words of detailed insights, this guide will help you understand the science, significance, and potential of this transformative technology.
What Is Magsorption Water Purification?
Magsorption water purification is an advanced water treatment method that utilizes magnetically responsive adsorbent materials to remove contaminants from water. These materials have dual properties:
-
Adsorption capability — the ability to attract and hold pollutants on their surface
-
Magnetic responsiveness — allowing them to be easily separated from water using magnets
By merging adsorption and magnetic extraction, magsorption achieves rapid purification with minimal energy usage and reduced operational complexity.
The concept originated from nanotechnology and material science research aimed at improving traditional adsorption methods. Unlike conventional filters that require mechanical separation or chemical processes, magsorption simplifies the entire cycle—making it ideal for modern, sustainable water treatment systems.
How Magsorption Water Purification Works
To understand the effectiveness of magsorption, it is important to break down its process. The technique typically involves four interconnected steps:
1. Creation of Magnetic Adsorbents
Researchers engineer adsorbent particles—often nanoparticles or micro-sized materials—infused with magnetic properties. Common materials include:
-
Iron oxide nanoparticles
-
Magnetic graphene composites
-
Zeolite-based magnetic adsorbents
-
Magnetically modified activated carbon
These materials are designed to attract pollutants such as heavy metals, organic chemicals, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
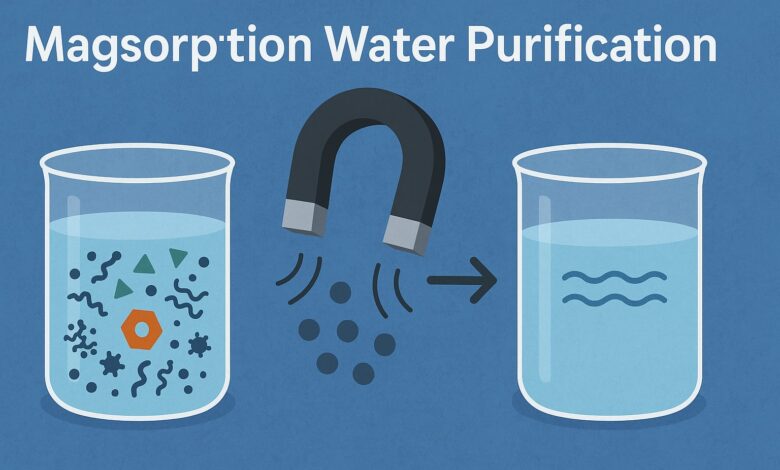
2. Introduction into Contaminated Water
The magnetic adsorbents are dispersed into the polluted water. Thanks to their large surface area and high reactivity, they quickly bind with contaminants through physical or chemical interactions.
3. Magnetic Separation
After adsorption, a strong external magnet is used to pull the particles out of the water. This step is:
-
Fast
-
Energy efficient
-
Highly precise
-
Practically clog-free
Traditional filtration systems often slow down due to blockages, but magsorption bypasses this problem entirely.
4. Regeneration or Disposal
Once removed, the contaminated adsorbents can be:
-
Cleaned and reused
-
Safely disposed of
-
Recycled using chemical processes
Many magnetic adsorbents have regeneration cycles that maintain up to 80–95% efficiency over multiple uses, making the process environmentally sustainable.
Why Magsorption Water Purification Is a Game Changer
1. Exceptional Removal Efficiency
Magsorption is renowned for its ability to remove a wide range of pollutants, such as:
-
Heavy metals (lead, mercury, arsenic)
-
Industrial dyes
-
Microplastics
-
Pathogenic microorganisms
-
Organic pollutants
-
Pesticides and pharmaceutical residues
This versatility makes it suitable for both household water systems and large-scale industrial uses.
2. Faster Processing Times
Unlike gravity-based filtration or multi-stage purification, magsorption delivers quick results. The magnetic separation step takes only minutes, significantly speeding up treatment cycles.
3. Reduced Environmental Impact
Conventional water purification often involves chemical agents, high-pressure systems, and large amounts of waste. Magsorption offers:
-
Fewer chemical additives
-
Lower energy requirements
-
Reusable adsorbents
-
Minimal sludge generation
This aligns with global sustainability goals and supports cleaner industrial operations.
4. Cost Efficiency
Because the magnetic adsorbents can be regenerated and reused, operational costs are reduced. Additionally, the lack of complex filtration membranes or high-pressure equipment means lower maintenance needs.
5. Scalable and Adaptable Technology
Magsorption water purification is suitable for:
-
Rural communities
-
Urban wastewater plants
-
Factories and industrial zones
-
Emergency relief systems
-
Portable water purification devices
Its adaptability allows it to serve as a critical tool for improving water access in both developing and developed nations.
Applications of Magsorption Water Purification
1. Industrial Wastewater Treatment
Industries such as textiles, mining, pharmaceuticals, and petrochemicals release pollutants that traditional systems struggle to filter. Magsorption effectively removes:
-
Colored dyes
-
Toxic metals
-
Chemical waste
-
Solvents
This helps industries meet environmental safety standards.
2. Municipal Water Treatment
Cities can integrate magsorption into existing purification infrastructures to enhance efficiency and reduce chemical usage.
3. Household Water Filters
With advancements in consumer technology, magnetic filters could become common in home filtration systems for safer drinking water.
4. Emergency Water Purification
During natural disasters, wars, or water supply contamination, portable magsorption-based devices can provide instant access to safe water.
5. Environmental Cleanup
Polluted rivers, lakes, and groundwater can be restored through large-scale magsorption deployment, offering a faster and more eco-friendly method of remediation.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its promise, magsorption water purification is still developing and faces certain challenges:
1. Production Costs of High-Quality Adsorbents
While costs are decreasing, large-scale production is still expensive for developing countries.
2. Nanomaterial Safety
The potential environmental impact of releasing nanoparticles requires strict monitoring and regulation.
3. Regeneration Efficiency
Some materials lose efficiency after repeated regeneration cycles, requiring further improvements.
4. Infrastructure Limitations
Countries with outdated water systems may struggle to integrate this advanced technology immediately.
However, continuous research is overcoming many of these challenges, bringing the technology closer to widespread adoption.
Future of Magsorption Water Purification
The future looks promising, with advancements expected in:
-
Biodegradable magnetic materials
-
AI-enhanced purification monitoring
-
More efficient adsorption structures
-
Large-scale environmental cleanup programs
-
Commercial household units
-
Integration with renewable energy systems
As sustainability takes center stage in global policy and innovation, magsorption water purification is poised to become a core component of next-generation water treatment solutions.
Conclusion
In a world increasingly threatened by water scarcity and pollution, magsorption water purification stands out as a revolutionary method combining the best of material science and magnetic technology. It offers faster, cleaner, and more efficient water treatment while reducing environmental impact and operational costs. Whether used for industrial wastewater, municipal systems, or emergency relief, magsorption represents a major leap forward in the quest for safe and sustainable water for all.



